NHS Surfaces
for coupling via the N-terminus of biochemical species
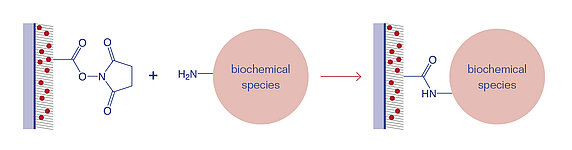
NHS-esters react immediately with primary amine (-NH2) groups of biochemical species to bind them covalently to the surface. However, due to its high reactivity the NHS ester is susceptible to hydrolysis, and thus, should be processed quickly.
PolyAn equips glass slides, coverslips, polymer slides and 96-well plates with reactive surfaces. Please do not hesitate to contact us, if you would like to functionalize a different format or substrate with our 2D-NHS or 3D-NHS surface.
Selected Publications
NHS surface for the immobilization of Glycans:
- Swan, J. et al., `The sialome of the retina, alteration in age-related macular degeneration (AMD) pathology and potential impacts on Complement Factor H´, bioRxiv, 2025, DOI: 10.1101/2025.03.09.642149.
- Khan, N. et al., `Sialoglycan-binding patterns of bacterial AB5 toxin B subunits correlate with host range and toxicity, indicating evolution independent of A subunits´, J. Biol. Chem., 2022, 298, 101900. DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101900.
- Sasmal, A. et al., `Simple and practical sialoglycan encoding system reveals vast diversity in nature and identifies a universal sialoglycan-recognizing probe derived from AB5 toxin B subunits´, Glycobiology, 2022, 32, 1101. DOI: 10.1093/glycob/cwac057.
- Ji, Y. et al., `Reversible O‑Acetyl Migration within the Sialic Acid Side Chain and Its Influence on Protein Recognition´, Chem. Biol., 2021, 16, 1951. DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.0c00998.
- Saha, S. et al., `Exploring the Impact of Ketodeoxynonulosonic Acid in Host-Pathogen Interactions Using Uptake and Surface Display by Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae´, mBio, 2021, 12, 03226-20. DOI: 10.1128/mBio.03226-20.
- Siddiqui, S.S. et al., `Sialoglycan recognition is a common connection linking acidosis, zinc, and HMGB1 in sepsis´, PNAS, 2021, 118, 2018090118. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2018090118.
- Ruprecht, C. et al., `Practical considerations for printing high-density glycan microarrays to study weak carbohydrate-protein interactions´, Carbohydrate Res., 2019, 481, 31. DOI: 10.1016/j.carres.2019.06.006.
NHS surface for the immobilization of Oligonucleotides (DNA/RNA):
- Jin, Z. et al., `Cross-amplified Barcodes on Slides for Spatial Transcriptomics Sequencing´, bioRxiv, 2022, DOI: 10.1101/2022.08.25.504658.
NHS surface for the immobilization of Proteins and Antibodies:
- Vendrell-Fernández, S. et al., `Conversion of the OmpF Porin into a Device to Gather Amyloids on the E. coli Outer Membrane´, ACS Synth. Biol., 2022, 11, 655. DOI: 10.1021/acssynbio.1c00347.
NHS surface for the immobilization of Peptides:
- Rapsch, K. et al., `Identification of antimicrobial peptides and immobilization strategy suitable for a covalent surface coating with biocompatible properties´, Bioconjugate Chem., 2014, 25, 308. DOI: 10.1021/bc4004469.
