Carboxy Surfaces
for non-covalent coupling of positively charged biomolecules via electrostatic adsorption, or EDC/NHS-mediated coupling of Amine-containing molecules
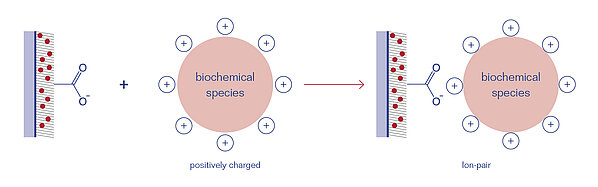
The Carboxy surface can be used for the adsorptive (non-covalent) immobilization of biochemical species via electrostatic interactions. The strength of the electrostatic (ion-ion) interactions can be tuned by the adhesion conditions, i.e. the ionic strenght and pH value of the probe buffer.
Carboxy groups can also be activated with 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide (EDC) and N-Hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) to form a highly reactive intermediate that can easily react with Amine groups of biochemical species.
PolyAn equips glass slides, coverslips, polymer slides and 96-well plates with reactive surfaces. Please do not hesitate to contact us, if you would like to functionalize a different format or substrate with our 2D-Carboxy or 3D-Carboxy surface.
Selected Publications
Carboxy surface for the immobilization of Proteins and Antibodies:
-
Esteso, V. et al., `Enhanced Fluorescence in a Lens-Less Fiber-Optic Sensor for C-Reactive Protein Detection´, Chemosensors, 2023, 11, 448. DOI: 10.3390/chemosensors11080448.
Carboxy surface for the immobilization of Oligonucleotides (DNA/RNA):
-
Karadimas, D. et al., `LATE-PCR for LoC Molecular Diagnostics Devices and Ist Application to the Sensitive Detection of SARS-CoV-2´, Eng. Proc., 2021, 6, 43. DOI: 10.3390/I3S2021Dresden-10076.
