Functionalized Surfaces for Protein Microarrays
Protein Microarrays are two-dimensional arrays of protein capture moieties (e.g. antibodies) printed onto a solid substrate used to assay a large number of analytes (e.g. antigens) within a sample.
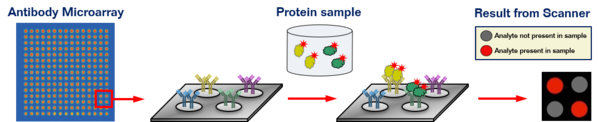
Protein microarrays come in two basic formats, "forward phase" (i.e. one antibody probing multiple samples) and "reverse phase" (i.e. one sample probed by multiple capture reagents). In "forward phase" arrays, captured reagents (antibodies, aptamers, or other proteins) are spotted at defined positions on a substrate, which is then interrogated with any of a variety of probes, from protein lysate and enzymes to small molecules and nucleic acids. In "reverse phase" arrays, on the other hand, protein lysates are spotted, and the arrays are then probed with antibodies to detect e.g. phosphorylated signaling molecules.
All of PolyAn’s reactive surfaces are completely transparent. They are characterized by a low lot-to-lot variation that is specified and monitored by using contact angle measurements as well as qualitative test methods.
A flyer showing the most commonly used functionalized surfaces for Protein Microarrays available from PolyAn can be downloaded here.
More hydrophobic surfaces may result in reduced spot diameter, depending on the spotting buffer composition. Results may vary based on buffers, sample preparation, spotting and scanning instruments.
Please note, that in order to facilitate handling of the glass slides PolyAn also offers a range of useful accessories and reagents.
Nitrocellulose Film Slides
PolyAn is the distributor of the nitrocellulose film slides from Grace Bio-Labs. The following table illustrates the different product families for Reverse-Phase Protein Arrays (RPPA) and other microarray applications:
AVID | NOVA | SuperNOVA | PATH | |
| Binding Capacity | ++++ | ++ | ++++ | + |
| Fluorescence background | + | ++ | +++ | ++++ |
| Dynamic range (log scale fluorescence) | 5-6 | 5-6 | 7+ | 4-5 |
| Hydrophobicity | + | + | + | ++ |
| Applications | Best for any application requiring high binding capacity and colorimetric detection. | Reduced fluorescence background with lower binding capacity than AVID. Good signal-to-noise ratio for fluorescence detection. | Second generation NOVA, lowest fluorescence background, high binding capacity. Best for fluorescence detection and large dynamic range. | Lowest fluorescence background, lower binding capacity, reduced dynamic range. Best signal-to-noise ratio for fluorescence detection. |
Selected Publications
- Allelein, S. et al., `Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA)-Positive Extracellular Vesicles in Urine: A Potential Liquid Biopsy Strategy for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis?´, Cancers 2022, 14, 2987. DOI: 10.3390/cancers14122987.
- Itri, S. et al., `A pin-based pyro-electrohydrodynamic jet sensor for tuning the accumulation of biomolecules down to sub-picogram level detection´, Sens. Biosens. Res. 2022, 38, 100536. DOI: 10.1016/j.sbsr.2022.100536.
- Horta, S. et al., `Evaluation of Immuno-Rolling Circle Amplification for Multiplex Detection and Profiling of Antigen-Specific Antibody Isotypes´, Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 6169. DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c00172.
- Malik, A. et al., `Immunological Evaluation of Synthetic Glycosylphosphatidylinositol Glycoconjugates as Vaccine Candidates against Malaria´, Chem. Biol. 2020, 15, 171. DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.9b00739.
- Goyette, A.-P. et al., `Microfluidic multipoles theory and applications´, Nature Commun. 2019, 10, 1781. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-09740-7.
- Hettegger, P. et al., `High similarity of IgG antibody profiles in blood and saliva opens opportunities for saliva based serology´, PLoS One 2019, 14, 218456. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218456.
- Herrmann; A. et al., `Bioorthogonal in Situ Hydrogels Based on Polyether Polyols for New Biosensor Materials with High Sensitivity´, Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 11382. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.8b01860.
- Peter, H. et al., `Lab-on-a-Chip Device for Rapid Measurement of Vitamin D Levels´, Meth. Mol. Biol. 2018, 35, 477. DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7614-0_35.
- Moscetti, I. et al., `Binding kinetics of mutant p53R175H with wild type p53 and p63: A Surface Plasmon Resonance and Atomic Force Spectroscopy study´, Biophys. Chem. 2017, 228, 55. DOI: 10.1016/j.bpc.2017.07.002.
- Peter, H. et al., `Lab-on-a-Chip Proteomic Assays for Psychiatric Disorders´, Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 33, 339. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-52479-5_33.
- Soria, J. et al., `Tear proteome analysis in ocular surface diseases using label-free LC-MS/MS and multiplexed microarray biomarker validation´, Sci. Reports 2017, 7, 17478. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-17536-2.
- Gerdtsson, A.S. et al., `Evaluation of Solid Supports for Slide- and Well-Based Recombinant Antibody Microarrays´, Microarrays 2016, 5, 16. DOI: 10.3390/microarrays5020016.
