3D-Epoxy Microplates
for covalent coupling of biomolucles via nucleophilic groups (e.g. amine groups)
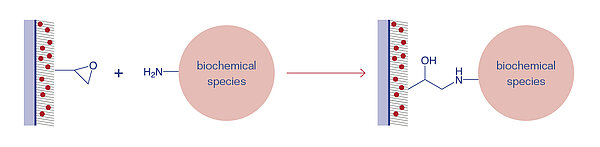
Epoxides are cyclic ethers with a highly strained three ring that can easily react with nucleophilic groups, e.g. amines, thiols, and hydroxyl groups. The Epoxy surface is uncharged and temperature-stable up to 40°C. Compared to NHS surfaces, the Epoxy surface is more stable against humidity and has a longer shelf-life of up to two years.
Products
PolyAn also equips glass slides, coverslips, polymer slides, and COP films with reactive 3D-surfaces. Please do not hesitate to contact us, if you would like to functionalize a different format or substrate with our 3D-Epoxy surface.
Handling Recommendations
The 3D-Epoxy Microplates are used mainly if adsorptive binding of peptides, oligonucleotides or proteins, for example, to high/medium binding surfaces is ineffective or the binding strength is not sufficient.
The nucleophilic addition is catalysed by acid or basic conditions. Under acidic conditions, the oxygen in the ring is positively charged, which facilitates the nucleophilic attack. Under basic conditions the least substituted carbon is attacked by the applied nucleophil in a standard SN2 reaction.
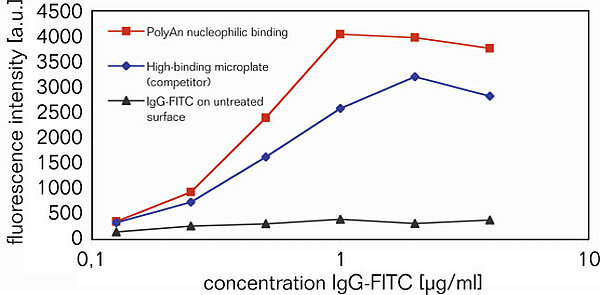
3D-Epoxy surface for ELISA applications
Comparison of IgG-FITC binding onto PolyAn's 3D-Epoxy surface versus passive (adsorptive) immobilization
Selected Publications
- Tuncay, A. et al., `Performance benchmarking microplate-immunoassays for quantifying target-specific cysteine oxidation reveals their potential for understanding redox-regulation and oxidative stress´, Free Rad. Biol. Med., 2023, 204, 252. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.05.006.
- Tuncay, A. et al., `RedoxiFluor: A microplate technique to quantify target-specific protein thiol redox state in relative percentage and molar terms´, Free Rad. Biol. Med., 2022, 181, 118. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.01.023.
- Noble, A. et al., `ALISA: A microplate assay to measure protein thiol redox state´, Free Rad. Biol. Med., 2021, 174, 272. DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.08.018.
